Centro risorseGuida pratica
Utilizzo di PowerShell per elencare le attività pianificate su macchine Windows
Utilizzo di PowerShell per elencare le attività pianificate su macchine Windows
Soluzione nativa
- Apri il PowerShell ISE e crea un nuovo file con il seguente script PowerShell, assicurandoti di inserire il nome del computer e il percorso di output:
$cred = Get-Credential
$comp = "PDC"
$session = New-PSSession -ComputerName $comp -Credential $cred
$script = {
"Services:"
Get-WmiObject win32_service -ErrorAction Stop| where {$_.StartMode -like 'Auto' -and $_.Startname -notlike '*local*' -and $_.Startname -notlike '*NT AU*'}| Select-Object Name, DisplayName, State, StartMode, StartName | Format-Table -Property * -AutoSize| Out-String -Width 4096
# To output to CSV, add this string to the previous command: | Export-Csv c:\Out\filename.csv - NoTypeInformation
"ScheduledTasks"
schtasks.exe /query /V /FO CSV | ConvertFrom-Csv | Where { $_.TaskName -ne "TaskName" -and $_.TaskName -like "*powershell*"}|Select-Object @{ label='Name'; expression={split-path $_.taskname -Leaf} }, Author ,'run as user','task to run'| Format-Table -Property * -AutoSize| Out-String -Width 4096
# To export to CSV, add this string to the previous command: | Export-Csv c:\Out\filename.csv - NoTypeInformation
}
Invoke-Command -Session $session -ScriptBlock $script
- Esegui lo script utilizzando le credenziali di un account che dispone dei diritti di amministratore sul computer locale in questione.
- Esaminare il rapporto risultante:

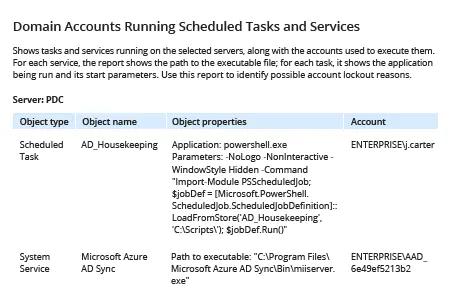
Netwrix Auditor per Windows Server
- Esegui Netwrix Auditor. Vai su “Reports” -> Clicca su “Predefined” -> Espandi la sezione “Windows Server” -> Clicca su “Windows Server – State-in-Time” -> Scegli “Domain Accounts Running Scheduled Tasks and Services” -> Clicca su “View”.
- Per limitare il rapporto a un particolare server o workstation: Digitare il nome della macchina nel campo “Nome server” nei filtri -> Fare clic su “Visualizza Rapporto”.
Condividi su
