DCSync is an attack that allows an adversary to simulate the behavior of a domain controller (DC) and retrieve password data via domain replication. The classic use for DCSync is as a precursor to a Golden Ticket attack, as it can be used to retrieve the KRBTGT hash.
Specifically, DCSync is a command in the open-source Mimikatz tool. It uses commands in the Directory Replication Service Remote Protocol (MS-DRSR) to simulate the behavior of a domain controller and ask other domain controllers to replicate information — taking advantage of valid and necessary functions of Active Directory that cannot be turned off or disabled.
Handpicked related content:
The Attack Process
The DCSYNC attack works as follows:
- The attacker discovers a domain controller to request replication.
- The attacker requests user replication using the GetNCChanges
- The DC returns replication data to the requestor, including password hashes.

Rights Required
Some very privileged rights are required to execute a DCSync attack. Since it typically takes some time for an attacker to obtain these permissions, this attack is classified as a late-stage kill chain attack .
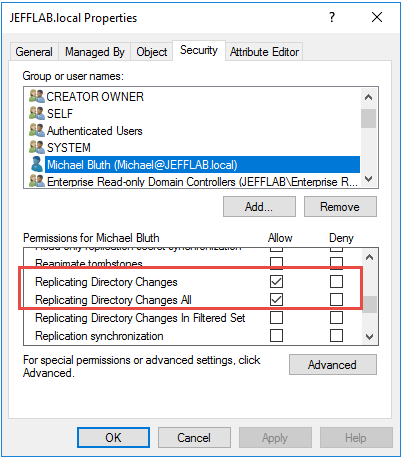
Generally, Administrators, Domain Admins and Enterprise Admins have the rights required to execute a DCSync attack. Specifically, the following rights are required:
- Replicating Directory Changes
- Replicating Directory Changes All
Replicating Directory Changes In Filtered Set
How Netwrix Solutions Can Help You Detect and Thwart DCSync Attacks
Detection
Netwrix Threat Manager monitors all domain replication traffic for signs of DCSync. It does not rely on event logs or network packet capture. Its primary detection method is finding patterns of behavior matching DCSync, including replication activity between a domain controller and a machine that is not a domain controller.
The solution provides a clear summary of the suspicious activity, as well as a visualization illustrating which user perpetrated the attack, the domain and user being targeted, and supporting evidence of the attack. If the same user executes multiple DCSync attacks, this critical information will also be included.
Response
To execute DCSync, an attacker needs elevated privileges, so the key to thwarting an attack is to immediately block privilege escalation. The standard playbook response of disabling the user account may not be enough, since by the time you spot the attack in progress, the attacker likely has a host of other resources and options available to them.
Netwrix Threat Prevention provides blocking policies that can prevent an account or workstation from executing additional replication, which can slow down an attack and give responders more time to completely eliminate the threat.
Netwrix Threat Manager supports these response steps by providing details about the DCSync attack perpetrator, sources, targets and queried objects.
See Netwrix Threat Manager in Action
Share on
Learn More
About the author

Kevin Joyce
Director of Product Management
Director of Product Management at Netwrix. Kevin has a passion for cyber security, specifically understanding the tactics and techniques attackers use to exploit organizations environments. With eight years of experience in product management, focusing on Active Directory and Windows security, he’s taken that passion to help build solutions for organizations to help protect their identities, infrastructure and data.
Learn more on this subject
Data Privacy Laws by State: Different Approaches to Privacy Protection
What Is Electronic Records Management?
Regular Expressions for Beginners: How to Get Started Discovering Sensitive Data
External Sharing in SharePoint: Tips for Wise Implementation
Trusts in Active Directory
